Physics articles at StarkEffects.com.
Physics Articles
Stark Effect
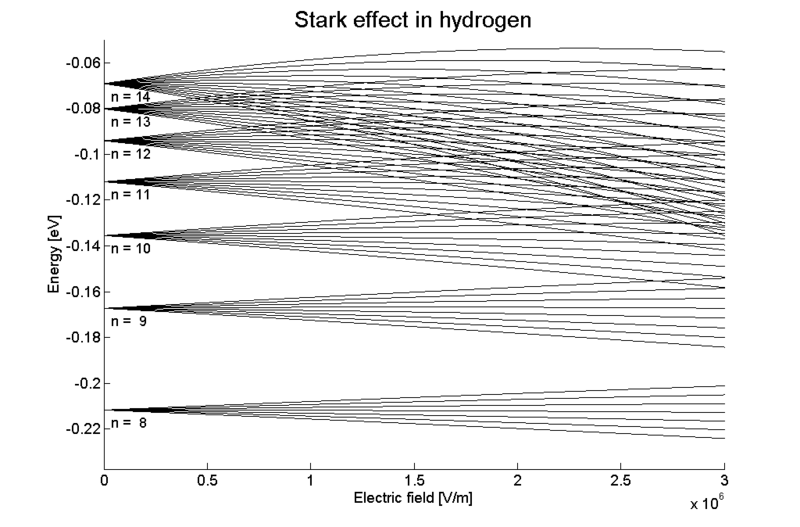 The Stark Effect is shown here in the splitting and shifting of spectral lines in hydrogen under the influence of an external electric field.
The Stark Effect is shown here in the splitting and shifting of spectral lines in hydrogen under the influence of an external electric field.
What is the Stark Effect? This article discusses the spectroscopic effect of strong electric fields known as the Stark effect, named for Johannes Stark, the first to experimentally demonstrate the effect.
Vector Form for Snell's Law
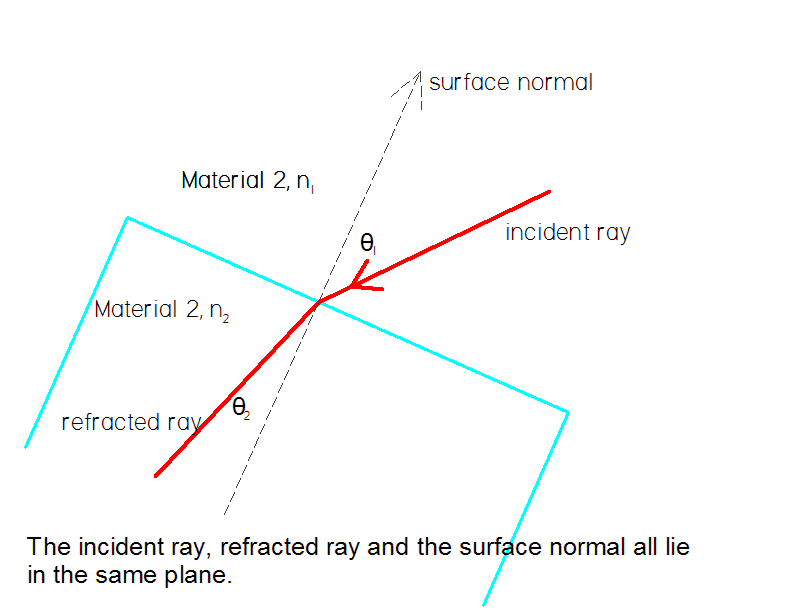
Snell's Law in Vector Form. Usually described in simple single plane coordinates, Snell's law is much more useful when you consider possible refraction out of the plane. To accomplish calculations of this type requires a vector form of the law of refraction.
Snell's law is the one of the first things you learn in an optics class. It is the basis of all refractive optics from your eyeglasses to microscopes and telescopes and even much of the information super highway made of fiber optics and the associated components. But the textbook version of Snell's law always seems to be in a contrived coordinate system with all the light travel in the plane of the page. To use a coordinate system that is more natural to the situation, you need a vector form for Snell's law.
Laser Beam Propagation
Basics of Laser Beam Propagation. Here are some of the formulas and descriptions of wave phenomena in coherent beams. This is a work in progress, so please have patience, but go ahead and tell me if you see something wrong!
The Hydrogen Atom Wavefunctions
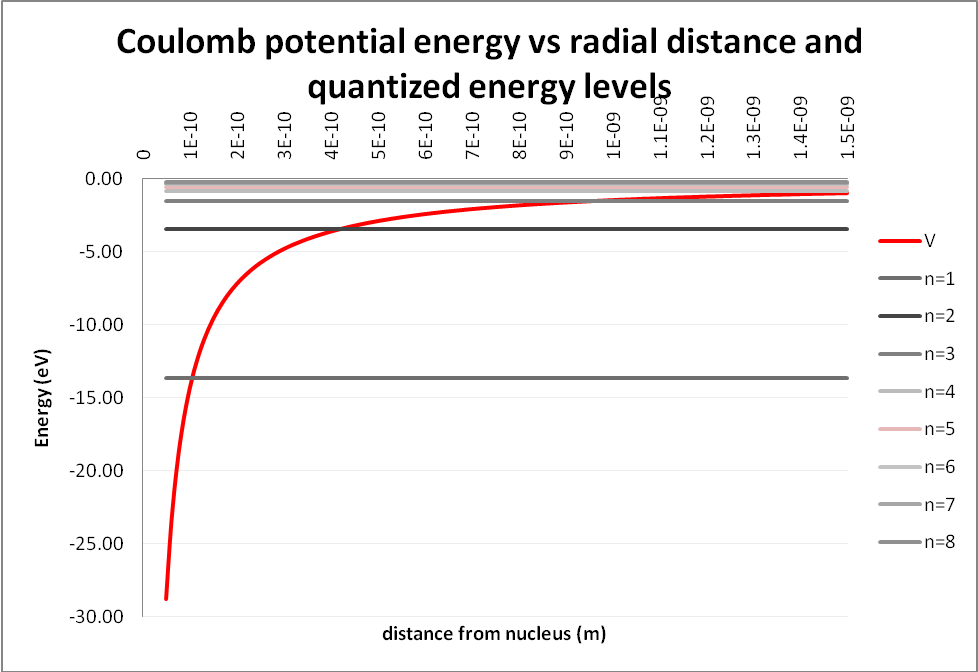
Hydrogen Atom Wavefunctions. So, your're sitting around the apartment one day, there is nothin' on the tube, and you start wondering "What are the energy levels of atomic hydrogen? I'd have to know that to figure out the wavelengths of the spectral lines emitted by a hydrogen atom." Then, suddenly, you realize, "Oh my goodness! I'd have to solve the Schrödinger equation and find the the wavefunctions for the hydrogen atom to find out something like that." Here are those wavefunctions and energy levels all spelled out for you.
If you were just wondering what the energy levels of the hydrogen atom are, and how to find them by solving the Shrödinger equation, you are in luck! On this page, we display the hydrogen atom wavefunctions and energy levels which can be scaled to any hydrogen-like atom (single electron ion).
Quick Science & Math References
- Our Solar System.
- Earth Facts.
- The Metric System.
- Trigonometric Identities.
- Vector & Tensor Identities.
- Explicit Forms of Vector Operators
- Light & Electromagnetic Spectrum.
- Common Laser Wavelengths.
- Human Physiology Facts.
- Human History Timeline
- Geologic Timeline
- Cambrian Explosion
- Life on Earth Timeline
- ASCII Codes and HTML Display Codes
- Thousands of HTML Symbol Codes
- HTML Symbol Codes for Greek Letters
- The Best Way to put Equations on your Web Page
Physics Basics Series
- Basics of Classical Mechanics.
- Basics of Quantum Mechanics.
- Basics of Electrodynamics.
- Basics of Optics.
- Basics of Mathematical Tools for Physics.
- Basics of Plasma Physics.
- Basics of Solid State Physics.
Math Basics Series
- Numbers
- Arithmetic
- Algebra
- Geometry
- Analysis
Technology Basics Series
- Basics of Remote Sensing.
- Basics of Digital Signal Processing.
- Critical Electronic Circuits
- Infrared Imaging Basics
Knowledge Branches
- Information Theory
- How Reading Works in the Brain
- Psychology of Learning
- Logic
WORK IN PROGRESS
- What is the Stark Effect?
- The Chemistry of Love &/or Addiction
- Critical Thinking: How to question what you see, read or hear.
- Aristotle's Prior Analytics - the birth of Logic.
- Optical Solutions, lenses that solve problems
- Fractals
- PTC - Photon Transfer Curve or Mean Variance Analysis
- 3-D Noise
- Laser Primer
- Rail Guns
- Special Relativity
- Radar Technology
- Acousto-optic Cells
- Harmonic Generation for Laser Frequency Doubling (SHG) and Tripling -using non-linear crystals.
- Measurement: Accuracy & Precision.
- Things you should know about computer modeling of physical phenomena!
- Giant Magneto-resistance
- Peltier Cooling
- Pyro-Electric Detectors
- Piezo-Electric Crystals
- Laser Speckle
- FFT and DFT the fast fourier transform and the discrete fourier transform
- Fabry Perot Etalon
- The Hydrogen Atom.
- PCA (Principal Component Analysis)
- Energy per mass in fuels such as Hydrogen, Gasoline, Kerosene, HMX etc...
- Nobel prize winning work on the CCD
- How does a CCD work and what are the normal characteristics of a CCD
- Nobel Prize Winning work on Giant Magneto-resistance
- FROG -frequency resolved optical gating
- Optical Wavefront Sensing
- THz imaging and time-domain spectroscopy
- Camera Calibration
- Laser Designators
- Resampling

