StarkEffects.com
Articles by Subject Category
Physics Basics Series
- Basics of Classical Mechanics.
- Basics of Quantum Mechanics.
- Basics of Electrodynamics.
- Basics of Optics.
- Basics of Mathematical Tools for Physics.
- Basics of Plasma Physics.
- Basics of Solid State Physics.
Troy Stark's Science & Society Opinion Blog
Concise Articles, Tutorials & Primers on Physics, Math & Technology & Obscure Science Topics
The Golden Ratio, Φ
Math is infiltrating popular culture. You can't keep up on the latest popular fiction or even Hollywood movies now without being exposed to words from mathematical literature. Well, if you have been reading an otherwise fun book and, suddenly, you came across a reference to the golden ratio, or Φ, perhaps you would like to know a little about what it is. A fascinating number, Φ, derived originally from geometrical considerations, is now the subject of active mathematical research. This page describes just the basics.
This number shows up in nature everywhere. It also shows up in the most interesting human endeavors including aesthetics and now, popular film and fiction.
Φ, (Phi, usually pronounced “fee”). This is a fascinating number. Φ is an irrational number, simply meaning that it can’t be written as whole number or as a fraction using whole numbers. There are other interesting irrationals such as π, but I find Φ to be the most fascinating.
Let’s look first at a geometrical description of Φ. The rectangle below is known as the “most beautiful” rectangle. Divide the width by the height and you get the Golden ratio or Φ.
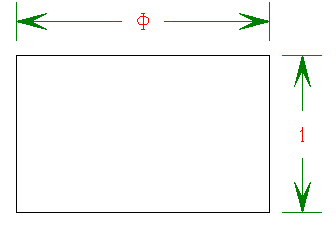 The Most Beautiful Rectangle.
The Most Beautiful Rectangle.
Of course, this is only interesting for the following reason: if you cut off the largest square the rectangle that is left over has the same ratio of lengths.
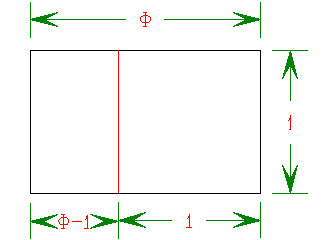
Where 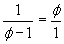 .
.
We could solve this and get: 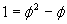 or
or 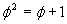 .
.
This is an interesting situation. If you solve this, using the quadratic formula, you get:

Of course, the situation we have above forces us to accept the + sign in this equation and we get

where the decimal representation goes on forever without ever repeating.
While these are rather fascinating to think about, there is an even more interesting way to write this golden ratio. Take the first equation we have above defining the golden ratio 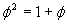 and we can take the square root, accepting only the positive root:
and we can take the square root, accepting only the positive root:
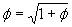 but we can substitute for
but we can substitute for 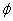 on the right hand side to get:
on the right hand side to get: 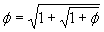 but we can substitute for
but we can substitute for 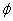 on the right hand side to get:
on the right hand side to get: and so on forever
and so on forever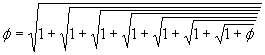

Or, we could have taken
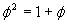 and divided by
and divided by 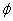 to get:
to get:
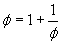 and if we iterate substitution the same way as before:
and if we iterate substitution the same way as before:
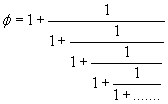
So we found the only irrational number I know of that can be written with nothing but 1’s.
Here is what we get if keep the golden ratio on the right hand side:

but if we truncate somewhere along the way, we wont quite reach, but we get closer and closer with each iteration:

Below, I show how I go about constructing a golden rectangle beginning with a
1 ×1 square:

What can you tell about the triangle that is created by drawing my first line from the center of one side of the square to one corner of the square?
Goldene Schnitt
The first appearance of the "Golden Ratio" in any known literature occurs in Euclid's writing circa 300BCE:
"A straight line is said to have been cut in extreme and mean ratio when, as the whole line is to the greater segment, so is the greater to the lessser."
However, the first recorded use of the term "Golden Ratio" or rather "Goldene Schnitt" is the in the work of Martin Ohm (brother of Georg Simon Ohm, of electrical resistance fame) in his second edition of the book Die Reine Elementar Mathematik (The Pure Elementary Mathmatics) in 1835.
It is probably due to the fascinating properties of the ratio that so many authors have attributed discovery of these properties to cultures from the ancient Egyptians builiding the pyramids to the Babylonians circa 3000 BCE (both of whom definitely did have many important geometrical theories figured out) to Pythagoras himself in ~500 BCE. But the reality is, the first writings showing the properties of this ratio are due to Euclid.
Quick Science & Math References
- Our Solar System.
- Earth Facts.
- The Metric System.
- Trigonometric Identities.
- Vector & Tensor Identities.
- Explicit Forms of Vector Operators
- Light & Electromagnetic Spectrum.
- Common Laser Wavelengths.
- Human Physiology Facts.
- Human History Timeline
- Geologic Timeline
- Cambrian Explosion
- Life on Earth Timeline
- ASCII Codes and HTML Display Codes
- Thousands of HTML Symbol Codes
- HTML Symbol Codes for Greek Letters
- The Best Way to put Equations on your Web Page
Physics Basics Series
- Basics of Classical Mechanics.
- Basics of Quantum Mechanics.
- Basics of Electrodynamics.
- Basics of Optics.
- Basics of Mathematical Tools for Physics.
- Basics of Plasma Physics.
- Basics of Solid State Physics.
Math Basics Series
- Numbers
- Arithmetic
- Algebra
- Geometry
- Analysis
Technology Basics Series
- Basics of Remote Sensing.
- Basics of Digital Signal Processing.
- Critical Electronic Circuits
- Infrared Imaging Basics
Knowledge Branches
- Information Theory
- How Reading Works in the Brain
- Psychology of Learning
- Logic
WORK IN PROGRESS
- What is the Stark Effect?
- The Chemistry of Love &/or Addiction
- Critical Thinking: How to question what you see, read or hear.
- Aristotle's Prior Analytics - the birth of Logic.
- Optical Solutions, lenses that solve problems
- Fractals
- PTC - Photon Transfer Curve or Mean Variance Analysis
- 3-D Noise
- Laser Primer
- Rail Guns
- Special Relativity
- Radar Technology
- Acousto-optic Cells
- Harmonic Generation for Laser Frequency Doubling (SHG) and Tripling -using non-linear crystals.
- Measurement: Accuracy & Precision.
- Things you should know about computer modeling of physical phenomena!
- Giant Magneto-resistance
- Peltier Cooling
- Pyro-Electric Detectors
- Piezo-Electric Crystals
- Laser Speckle
- FFT and DFT the fast fourier transform and the discrete fourier transform
- Fabry Perot Etalon
- The Hydrogen Atom.
- PCA (Principal Component Analysis)
- Energy per mass in fuels such as Hydrogen, Gasoline, Kerosene, HMX etc...
- Nobel prize winning work on the CCD
- How does a CCD work and what are the normal characteristics of a CCD
- Nobel Prize Winning work on Giant Magneto-resistance
- FROG -frequency resolved optical gating
- Optical Wavefront Sensing
- THz imaging and time-domain spectroscopy
- Camera Calibration
- Laser Designators
- Resampling
